AI-Agent + Analyst
Powering the Modern SOC
Today’s security operations teams are under increasing pressure to respond to an overwhelming volume of critical alerts from a rapidly evolving threat landscape. With AI as a tool to assist threat adversaries in attacks, SecOps teams need to harness Agentic AI to augment their daily security operations.


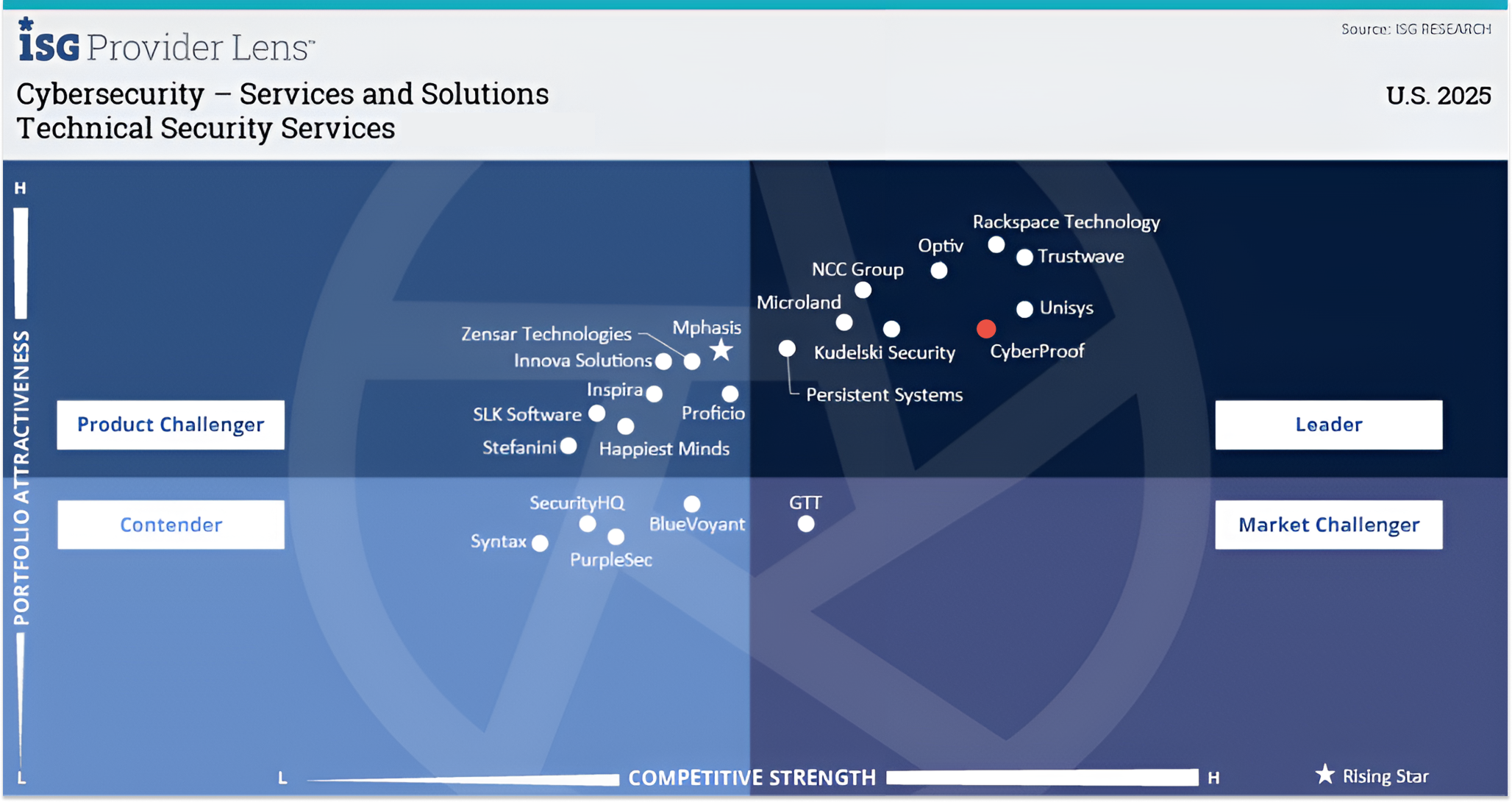
ISG Cybersecurity Report 2025
For the second year running!
CyberProof is recognized as a leader in three categories:
- Next-Gen SOC/MDR Services
- Strategic Security Services
- Technical Security Services

CyberProof 2025 Mid-Year Cyber Threat Landscape Report
1H 2025 Analysis
Key insights into Ransomware Groups, Top Trends, and 2024 Predictions vs 2025 Reality


Defend The Threats That Matter Most!
CyberProof is the only company in the industry to deliver an integrated threat-led platform (powered by Interpres) for managing your real-estate of assets, risk exposure and defense services together within your enterprise.

Cloud First Security
CyberProof is a cloud first security operations company, enabled through key cloud partners, to help deliver the most cutting edge security services to help protect your enterprise.

Detect, Respond, Adapt – Everywhere
CyberProof’s MXDR platform powered by AI adapts to the most complex evolving threat landscape, continuously aggregating threat intelligence and responding, identifying and mitigating risk within your enterprise.
Today’s Cybersecurity Dilemma: Analyzing over 100,000 security incidents daily from more than 150 distinct threat actors
The Challenges:
- Security teams struggle to keep up with threats
- Uncertainty about relevant and significant threats
- Blind spots from ineffective, scattered cybersecurity tools

THE SOLUTION:
Defend Against the Threats That Matter Most
Cyberproof provides an integrated threat-led platform that combines:
Estate (Asset) Management:
Tag, classify, and prioritize known and unknown assets to understand your exposure – continuously
Exposure Management
Focus on relevant threats using CTEM and ASCA frameworks – continuously
Defense Management
Optimize detection and response playbooks – continuously
Resulting in GRC Transformation
Mitigate Global Risk, Define Business Outcomes & ROI, Mature Security Posture
Partners

















































“Today I have complete visibility into the entire environment, in real time”
Jamil Farshchi | Equifax CISO
Case Studies

Threat-led SIEM transformation delivers 85% cost savings for international retailer

90% increase in visibility after deploying Microsoft XDR with CyberProof

Organization saves millions on data ingestion & storage following cloud migration

SOC & NOC unification reduces exposure and accelerates defense for U.S. insurer

Global pharmaceutical and diagnostics company gains threat-led visibility and reduces global exposure

Global dental and pharmaceutical company enhances detection, reduces exposure, and improves compliance
Recognised as industry leaders