Updated February 3, 2025
Executive Summary
On January 24, 2025, CyberProof researchers spotted a likely new campaign of digitally signed malicious droppers used by attackers to spread infostealers against global organizations. The droppers were likely spread through social engineering tricks impersonating Zoom, Teams, Bravo, Wechat, and other virtual meeting & calling applications. Similar observations were reported by a security researcher in a tweet a few days later on the 27th of January. The final payloads observed during our investigation were NetSupport RAT, LummarStealer, CobaltStrike, and Remcos RAT.
CyberProof researchers assess with high confidence that this new campaign is likely only intended to target users to steal their credentials and may be used for a futuristic attack. At the time of writing this report, only windows users were targeted by this new campaign.
We will continue to monitor this campaign and will provide updates on any additional activities or changes in tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used by these cyber criminals. Current CyberProof customers are protected from this campaign.
Technical Details
Our team’s research, over the course of a year, has revealed that top infostealers are changing their tactics to bypass detection technologies and stay under the radar of security analysts. Below we will share our observations on the top infostealers and TTPs connected to this campaign.
The top infostealers observed were LummaStealer, Danabot, StealC, Amadey, Remcos, NetSupport RAT, Raccoon, etc. In 2023 and early 2024, these infostealers were predominantly spreading through IDAT loader (aka HijackLoader) campaigns that challenged researchers with many anti-analysis tricks including steganography to make analysis difficult.
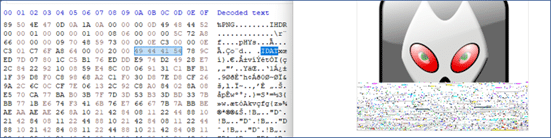
The name IDAT loader is derived from the fact that the loader checks for IDAT string in the shellcode before decrypting the next stage payload.
In recent months these infostealer attacks surged through FakeCaptcha campaigns with instructions.
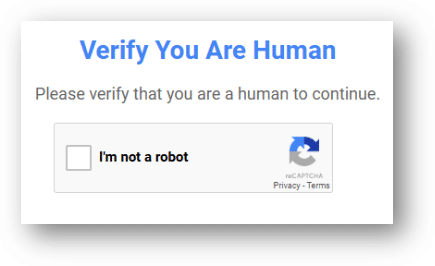
Clicking the “I’m not a robot” button in the FakeCaptcha, copies a PowerShell script to the clipboard and displays so-called “verification steps” that include:
- Press Win + R (this opens the Run dialog box);
- Press CTRL + V (this pastes the line from the clipboard into the text field);
- Press Enter (this executes the code).
The most recent infostealer campaign identified on the 24th of January looks to spread through possible malvertising pages serving digitally signed droppers impersonating as fake meeting applications. Some of the applications impersonated for deception include:

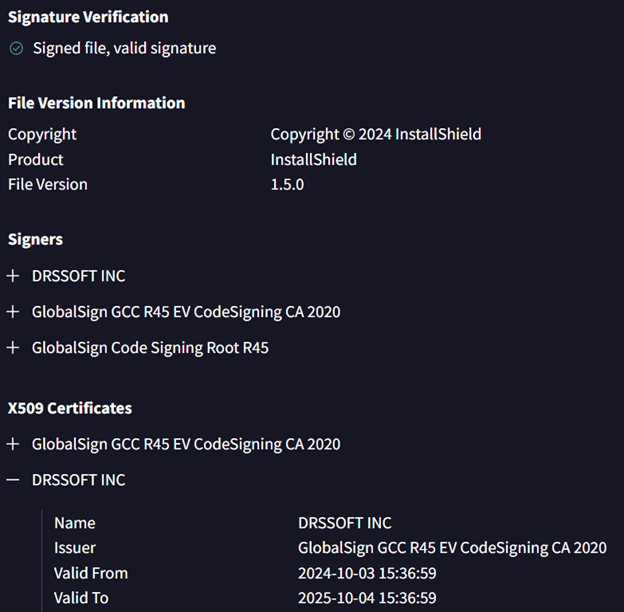
Further investigation revealed attackers using these droppers to spread infostealers namely NetSupport RAT, LummaStealer, CobaltStrike, and Remcos RAT. Clearly indicating the motivation of the campaign is to target victims for user credentials. Some of these droppers are digital signers. Those observed to have been abused in this campaign include:
- DRSSOFT INC
- PREMERA LLC
- ANALYZER ENTERPRISES LLP
Here’s an example of a sample signed by DRSSOFT INC:
Indicators of Compromise
MD5 of Droppers observed include:
- 4c6d58378be4b9051debfb5670f5b82c
- 3019c6c4f427e2407a1674e09ed4e545
- 258b7dd229fe3678dd729b5625df0846
- 440df12d81e75b5c98a36e4760a7e6ca
- 3b611cb90a2a15ed16b10e8597fb6578
- f4a4f19999a4f101d6df09b08366938b
- 6624cc2996ef930654b9ef3ef8171163
- Fa9267820f3ec58aeda90772a3c9fc44
- 0f145a85cfe6900ed7ab6444a32d03ec
- f2b346296bd558530a96cffc5c4bd18f
- a8269459960c65419748c0b4a18516a5
Recommendations
We recommend the following to safeguard against these threats:
- Invest in Employee Training: Employees are often the first line of defense against cyber threats. Training staff to recognize phishing emails, suspicious links, and other common attack vectors is critical. Regularly updated cybersecurity training programs ensure employees stay aware of evolving threats and adhere to best practices.
- Leverage Advanced Platforms: Modern threat detection platforms equipped with real-time monitoring, AI-driven threat intelligence, and automated response mechanisms are indispensable. These tools enable organizations to detect and neutralize threats swiftly, minimizing potential damage.
- Perform Regular Audits: Routine evaluations of your cybersecurity framework help identify and address vulnerabilities. Audits also ensure compliance with regulatory standards and improve the overall robustness of your security posture.
How CyberProof Can Help
As cyber threats continue to evolve, so too must the strategies and technologies used to combat them. Threat detection is a critical component of any organization’s cybersecurity strategy. Learn how CyberProof can help your organization effectively detect and respond to cyber threats.