What is vulnerability management?
Vulnerability management is the systematic process of discovering, categorizing, and addressing security weaknesses in digital systems and networks. By consistently applying this approach, organizations not only bolster their defense mechanisms but also significantly reduce the risk of cyber threats and potential data breaches.
Why do you need vulnerability management in today’s complex threat landscape?
Over the past few years, organizations have experienced a massive shift – AI, hyper-fast growth, and hybrid workplaces have altered the technological sphere and vulnerability management more than ever before. This rapid growth has made way for a record increase in vulnerabilities, some of which are yet to be identified.
Simultaneously, the threat landscape has become more advanced and complex than ever. AI-driven attack mechanisms, advanced threat tactics, and nation-state cyber warfare, among others, have created an unprecedented number of threats. Cybercriminals are becoming more organized, resourceful, and determined, and they are targeting organizations of all sizes and industries.
Challenges in the vulnerability management process
When it comes to security, enterprise organizations face another challenge: Complexities related to cloud and network architecture make it harder to keep track of their assets. With a combination of on-premises, cloud, and multi-cloud configurations, many enterprises don’t know what is connected to which network. That makes it harder for vulnerability analysis tools to map and manage environments.
All of these factors have contributed to a virtually unmanageable vulnerability landscape: one with too many alerts, and not enough ways to prioritize remediating them.
This is underscored by the fact that:
- Organizations have more assets than ever before – 53% of organizations reported security concerns related to asset management according to Forrester
- Cloud native, hybrid, and on-prem. systems all run simultaneously in any given organization
- Known vulnerabilities have grown from 2.5K in the 1990s to 192K in 2022, with 25,227 identified in 2022 – more than any other year
How vulnerability management works to support cloud environments
In today’s cloud-native era, ensuring that your organization is proactively addressing vulnerabilities is essential. The adoption of real-time posture management has become essential to increasing visibility in cloud environments. Continuous vulnerability scanning tools can help identify new vulnerabilities as they emerge, ensuring you have real-time visibility into potential risks. For example, an advanced vulnerability management scanning solution using a combination of agents or network-based scanning tools to cover multiple on-prem. and cloud environments.
Cloud Workload Protection (CWP) provides visibility across multi-cloud environments, allowing enterprise organizations to proactively identify and remediate risks to large-scale data and security operations.
This comprehensive approach enables enterprises to mitigate risks effectively, minimizing the potential impact of vulnerabilities on their security posture by shortening remediation times. By leveraging the expertise and capabilities of advanced Vulnerability Management services, organizations can bridge the gap between vulnerability detection and remediation, strengthening their overall security posture.
The vulnerability management process
The vulnerability management lifecycle provides a robust approach to threat management, ensuring that your assets are effectively protected at each stage:
- Asset Discovery and Inventory Management: Audit your organization’s assets, encompassing hardware, software, and network devices. This is achieved through automated scans and discovery techniques that assist in establishing a precise and current inventory of all assets.
- Vulnerability Assessment: Perform in-depth assessments and analyses of identified vulnerabilities to determine their severity, impact, and potential exploitability.
- Risk Analysis and Prioritization: Assess the severity, potential impact, and organizational risk of vulnerabilities.
- Regulatory Requirements & Reporting: Create detailed reports that provide identified weaknesses, their consequences, and suggested steps to help you meet regulatory, compliance, and risk management requirements.
- Remediation and Patch Management: Provide assurances that all assets stay up to date with the most recent security patches.
How are vulnerabilities ranked and categorized?
Managing the vast number of vulnerabilities in your organization’s network is a daunting task. Often, firms are unaware of all existing vulnerabilities. The Common Vulnerabilities & Exposure (CVE) database and the Common Vulnerabilities Scoring System (CVSS) are two publicly accessible tools that can help identify and rank the severity of a vulnerability.
However, recognizing a vulnerability’s severity isn’t sufficient.
Creating vulnerability management programs based on business risk
In addition to assessing severity, it’s important to define and assess risk according to your organization’s unique business priorities – considering threat probability, relevance to your assets, and potential impact on operations when building your vulnerability management program.
While the CVE database and CVSS can give us a general picture of baseline severity based on publicly-accessible intelligence, true risk can only be defined on an individual, organizational basis.
Here are a few elements to consider when it comes to vulnerability risk management:
- Narrow scope: The CVE database and CVSS score mainly focus on known exploitable vulnerabilities, overlooking emerging or unknown threats.
- Lack of context: Because the CVE database and CVSS score are standardized, they do not consider your organization’s unique business priorities, potentially leading to inaccurate risk assessments.
- Inflated severity: The CVSS scoring system can overstate the severity of vulnerabilities, complicating prioritization and resource allocation.
The best vulnerability management solutions use external cyber intelligence
Building out a threat-based approach to Vulnerability Management means leveraging threat intelligence to enrich your prioritization efforts and inform remediation plans. We know that the CVE database and baseline CVSS score offer insights into known exploitable vulnerabilities – but they lack the external context to inform threat prioritization for your organization. To best align business objectives and risk management when measuring potential impact, bringing in external threat intelligence to inform the internal scanning of your environment is essential.
Cyber threat intelligence (CTI) analysts work hand-in-hand with SOC analysts and Vulnerability Management teams to ensure that you have a deep understanding of the attack surface surrounding your enterprise. The analysts can then correlate data via a vulnerability management platform – from patch management systems, CMDBs, endpoint controls, applications, and web scanners – with external threat intelligence feeds from clear, deep, and dark web sources.
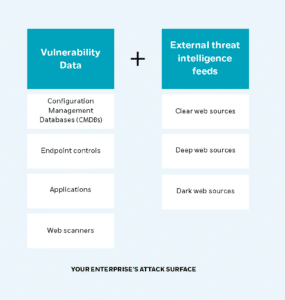
The makeup of an organization’s attack surface
How threat intelligence generates vulnerability management benefits
Threat intelligence spans a wide range of capabilities that can enrich internal scanning data, including:
- Reporting on new vulnerabilities and exploits faster than other data sources using real-time intelligence
- Tracking threat evolution to highlight patterns and predict future threats
- Identifying Proof of Concept (PoC) threats
- Detecting Zero-Day vulnerabilities before they are exploited in your organization’s software
- Correlating threat patterns from internal data with mitre att&ck techniques automatically to identify potentially vulnerable entry points
This holistic view not only identifies vulnerabilities but also prioritizes them by their ease of exploitation by attackers. CTI data can inform standardized scoring and other vulnerability management efforts by enriching publicly accessible knowledge with relevant information for your attack surface – allowing you to prioritize what is critical to your organization.
Why vulnerability management is crucial – adopting an attack-surface approach
Attack Surface Management vs. Vulnerability Management: as opposed to standard Vulnerability Management, Attack surface management (ASM) solutions take on the attacker’s point of view in order to detect vulnerabilities in a similar way. By continuously monitoring external-facing infrastructures, ASM can locate exposed assets and analyze for any exploitable vulnerabilities or emerging threats, bringing to light vulnerabilities that you may not know exist. To bolster these solutions, identifying critical assets and focusing scanners on them can help your organization successfully prioritize the greatest risks to the business.
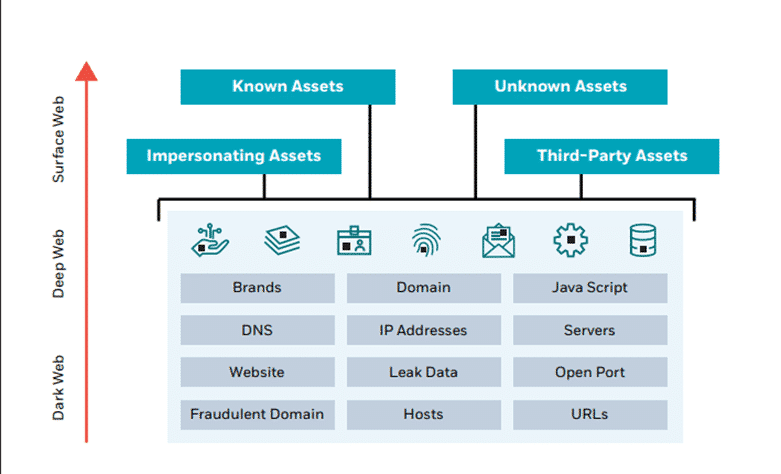
A sample organizational attack surface
How real-time scanning impacts the vulnerability management lifecycle
In today’s cloud-first era, vulnerability assessments should take place continuously to maintain good asset hygiene – ensuring that you know which assets your organization has under its belt. Qualys’ latest Threat Research Unit Report recommends a directed focus on the external attack surface by configuring notifications to be received whenever new and unknown assets or critical issues are detected. This practice ensures that your systems remain up to date and promptly address potential vulnerabilities. In a cloud-native environment, having an Advanced Vulnerability Management tool that is smoothly integrated with your cloud service ensures that the fluidity in your organization’s computing environments is not a bottleneck for security.
A look into the unknown
As the attack surface grows, staying aware of the amount and type of assets your organization manages has become increasingly challenging. All assets can be mapped into four quadrants, each posing more risk than the next:
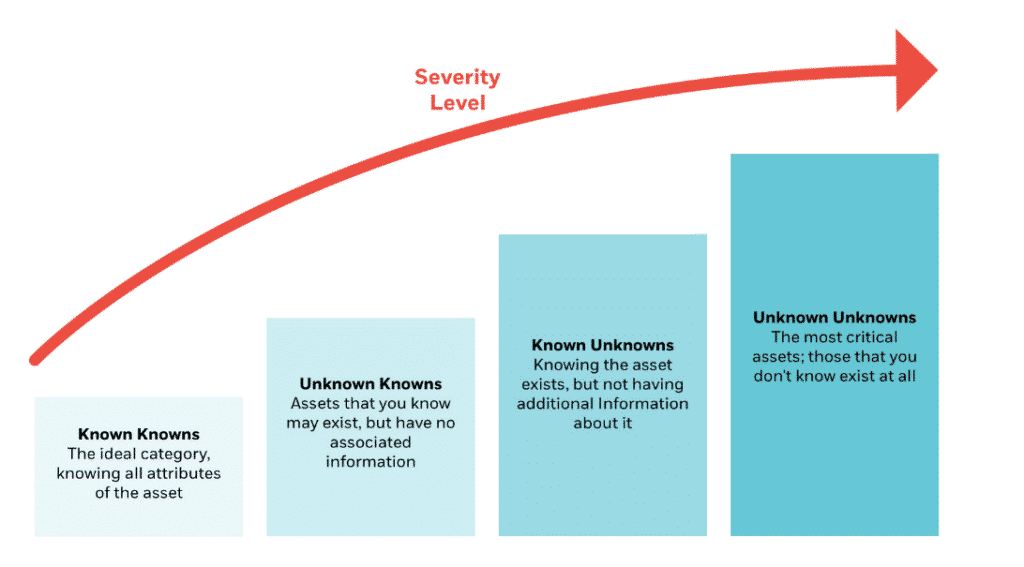
The four quadrants of asset organization
To respond to incidents and patch vulnerabilities, ensuring that your assets all fall into the “Known Knowns” category is key.
How an MDR provider can optimize vulnerability risk management
Traditional vulnerability management tools and approaches focus on “known vulnerabilities” listed in the CVE database – leaving your organization with potential blind spots. Because some assets may be totally unscannable, there will inevitably be vulnerabilities on those assets that cannot be identified.
That’s why enhancing your base vulnerability monitoring operations with the help of a Managed Detection & Response (MDR) provider can provide valuable benefits. Some MDR providers offer an end-to-end threat management framework that correlates data from various sources, including active vulnerability scanners, cloud assets, and endpoints. This integration provides cross-team data access, enabling the Security Operations Center, tailored Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) service, and advanced Threat Hunting teams to inform your organization’s Vulnerability Management approach. Coupled with CVSS severity scoring, this approach considers each vulnerability’s exploitability, asset importance, and exposure rating, providing a comprehensive overview of total vulnerabilities and organizational risk.
CyberProof’s Vulnerability Management service
At CyberProof, we take a risk-based approach to Vulnerability Management that ensures you are prioritizing appropriately and protecting your business by reducing your risk surface.
The steps and process of vulnerability management are more than just system and application patching. It is a complete process that includes patching, compensating controls, segmentation, segregation, and heightened diligence in security monitoring.
CyberProof prioritizes vulnerabilities based on real-world context. By taking into account factors such as each asset’s value to the business, the prevalence of specific attack types in the threat landscape, and the potential impact of exploitation, we help organizations efficiently address the most critical vulnerabilities. Context-aware prioritization is key to our proactively tackling cybersecurity threats head-on.
CyberProof provides extensive reporting and audit trails to demonstrate compliance with various regulatory standards – and has a governance model that provides an enterprise-wide view of risks. Our automated patch management capabilities facilitate timely and efficient updates across numerous systems, significantly minimizing the window of time attackers may have at their disposal to exploit known vulnerabilities.
A guide to vulnerability management – mitigating the risk of AI-powered attacks
Frequently asked questions
What is vulnerability management?
What is meant by vulnerability management?
What are the 5 steps of vulnerability management?
What are the main types of vulnerabilities?
What are vulnerability management tools?
What does a vulnerability management process look like?
Why is threat vulnerability management important?

Speak with an expert
Explore how CyberProof can help you anticipate, prevent, and mitigate ever-evolving cyberattacks in hybrid and cloud-native environments.
SPEAK WITH AN EXPERT